A hip replacement surgery, also known as hip arthroplasty, is a surgical procedure in which a damaged or diseased hip joint is replaced with an artificial joint, known as a prosthesis. This procedure is commonly performed when the hip joint becomes severely damaged or painful due to conditions such as osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, avascular necrosis, hip fractures, or other degenerative joint diseases.
During a hip replacement surgery, the damaged parts of the hip joint are removed and replaced with prosthetic components made of metal, plastic, or ceramic materials.
The main components of a hip prosthesis include:
• Femoral Component:
This part replaces the head of the femur (thigh bone) that fits into the hip socket. It consists of a metal stem with a ball-shaped head that mimics the natural shape of the femoral head.
• Acetabular Component:
This part replaces the damaged hip socket (acetabulum) with a concave metal shell lined with a plastic or ceramic liner. The artificial socket allows the new femoral head to move smoothly within it.
• Articular Liner:
The liner is often made of plastic or ceramic and is placed inside the acetabular component. It provides a smooth surface for the femoral head to glide against, allowing for smooth joint movement.
• Optional Fixation:
The prosthesis can be either cemented into place using bone cement or press-fitted without cement, relying on the natural bone’s ability to grow into the prosthesis over time.
Hip replacement surgery is typically performed by an orthopaedic surgeon and can be conducted using different approaches, such as the posterior approach, anterior approach, or lateral approach. The choice of approach depends on the surgeon’s preference and the patient’s specific condition.
What happens during hip replacement surgery?
Hip replacement surgery is done under anaesthetic. The type of anaesthetic you have depends on your needs and your anaesthetist’s recommendations. Once the patient is under anaesthetic, the surgeon makes a cut over the side of the hip, removing the upper part of the femur from the socket. This is then replaced with an artificial ball and socket joint. The operation itself usually takes less than two hours.
Benefits of hip replacement surgery
Hip surgery can help you get back to doing the things you love. Here are some of the benefits.
• Pain relief
Improved mobility and long-lasting results are key advantages, but the main benefit is pain relief. An arthritic hip can affect all areas of your life. Easing hip pain following successful surgery can provide immediate benefits and a better quality of life.
• High success rate
Hip replacement surgery boasts a high success rate. A massive 95% of patients report feeling very pleased with the outcome of their operation. Only 5% experience a complication of some sort, the severity of which affects the success of their surgery.
• Improved strength and mobility
After pain relief, increased mobility and strength is the next major benefit. Hip replacement patients should be able to carry out simple tasks like climbing the stairs and walking without the use of an aid.
• Long-lasting results
Artificial hip implants are designed to be long-lasting. The latest studies show 80-85% of hip replacements are still working 20 years after they were inserted. This means that older patients are unlikely to need hip revision surgery.
• Enhanced quality of life
Along with the other benefits mentioned, improved quality of life should not be underestimated. Reclaiming the ability to carry out simple tasks like walking and climbing the stairs can have extremely beneficial effects on a person’s mental well-being. With an increased range of movement, a patient can feel as though they have much more independence and are less of a burden on their support network.
Is hip replacement considered risky surgery?
With the benefits of hip replacement surgery covered, it’s now time to look at the risks. While hip replacement surgery is a major operation, it’s actually one of the most common orthopaedic procedures in the UK.
While hip replacement surgery can offer significant benefits, like any surgical procedure, it also carries certain risks and potential complications. It’s important for individuals considering hip replacement surgery to be aware of these risks and have open discussions with their healthcare provider. Some potential risks and complications of hip replacement surgery include:
• Infection:
Infections can occur at the surgical site or within the replaced joint. They may require antibiotic treatment, and in severe cases, the prosthetic joint may need to be removed and replaced.
• Blood Clots:
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE) are potential complications. Blood clots can form in the legs and travel to the lungs, which can be life-threatening.
• Dislocation:
The artificial joint may become dislocated, particularly in the initial post-operative period. Certain movements and positions might need to be avoided to prevent this.
• Implant Loosening:
Over time, the artificial joint may loosen from the bone. This can cause pain and require revision surgery to replace the implant.
• Implant Wear and Tear:
The artificial joint materials can wear down over time, potentially leading to debris in the joint, inflammation, and bone loss.
How to overcome the risk of hip replacement surgery with MIS Technique
Of course, the following tactics—which use the Minimally Invasive Surgery (MIS) approach and have the appropriate headings—can help reduce the risks associated with hip replacement surgery:
• Lower Risk of Infection:
• Smaller Incisions:
MIS requires fewer incisions than open surgery, which may lower the chance of infection at the operating site.
• Minimal Hospital Stay:
Individuals with MIS typically require fewer hospital stays, which lowers their risk of contracting hospital-acquired illnesses.
• Reduced Risk of Blood Clots:
• Early Mobilization:
MIS often permits reduced bed rest and faster post-operative mobilization, both of which can lower the risk of blood clots.
• Blood-Thinning Drugs:
To further reduce the risk of DVT and PE, your surgeon may recommend blood-thinning drugs.
• Increased Stability and Reduced Risk of Dislocation:
• Accurate Implant Positioning:
MIS methods offer more accurate implant positioning, which lowers the chance of joint dislocation.
• Better Preservation of Soft Tissue:
Less disturbance of surrounding tissues is frequently caused by the least invasive method, which enhances joint stability.
• Lower Risk of Implant Loosening:
• Precise Alignment:
MIS can lead to a more precise alignment of the prosthetic joint, which lowers the possibility of implant loosening over time.
• Preservation of Healthy Bone:
Less bone is removed during minimally invasive procedures, which helps to maintain a healthy bone structure.
• Reduced Wear and Tear of Implants:
• Less Damage to Muscle and Tissue:
Patients having MIS may heal more quickly and with less wear and tear on their prosthetic joints. This could result in less inflammation.
• Enhanced Implant Longevity:
The artificial joint’s long-term success can be attributed to precise implant placement and less wear and tear.
Conclusion
To sum up, depending on the specific situation, hip replacement surgery may or may not be a good option. Hip replacement surgery can be very beneficial for those who are experiencing severe hip pain, limited mobility, and a lower quality of life as a result of illnesses like osteoarthritis or hip fractures. These benefits include pain reduction and increased functionality. The potential benefits are further enhanced when Minimally Invasive Surgery (MIS) procedures are used for hip replacement. However, the choice necessitates a thorough assessment taking into account variables such as past medical history, general health, responsiveness to therapy, and readiness to follow post-operative rehabilitation.
For some patients, MIS may be an even more alluring choice due to its smaller incisions, lower risk of infection, improved implant durability, and maybe faster recovery. To find out if hip replacement surgery—including MIS procedures—is a good fit for a patient’s particular requirements and goals for better health, an open discussion with a medical expert knowledgeable in both traditional and MIS methods is still essential.

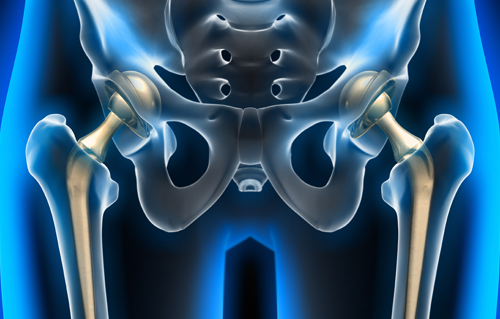



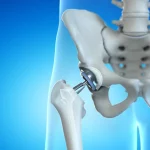
Hip replacement surgery offers significant benefits, including pain relief, improved mobility, and enhanced quality of life. It’s particularly effective for individuals with severe arthritis or hip joint damage. However, risks include infection, blood clots, and potential dislocation of the new joint. Recovery can be lengthy, requiring physical therapy. Additionally, implants may wear out over time, necessitating revision surgery. Careful consideration of these factors and consultation with a healthcare provider is essential before deciding on the procedure.
The insights on post-operative care and rehabilitation are incredibly helpful.Thank you for providing such valuable guidance.
Great share!” Thanks for sharing these kind of information with us.