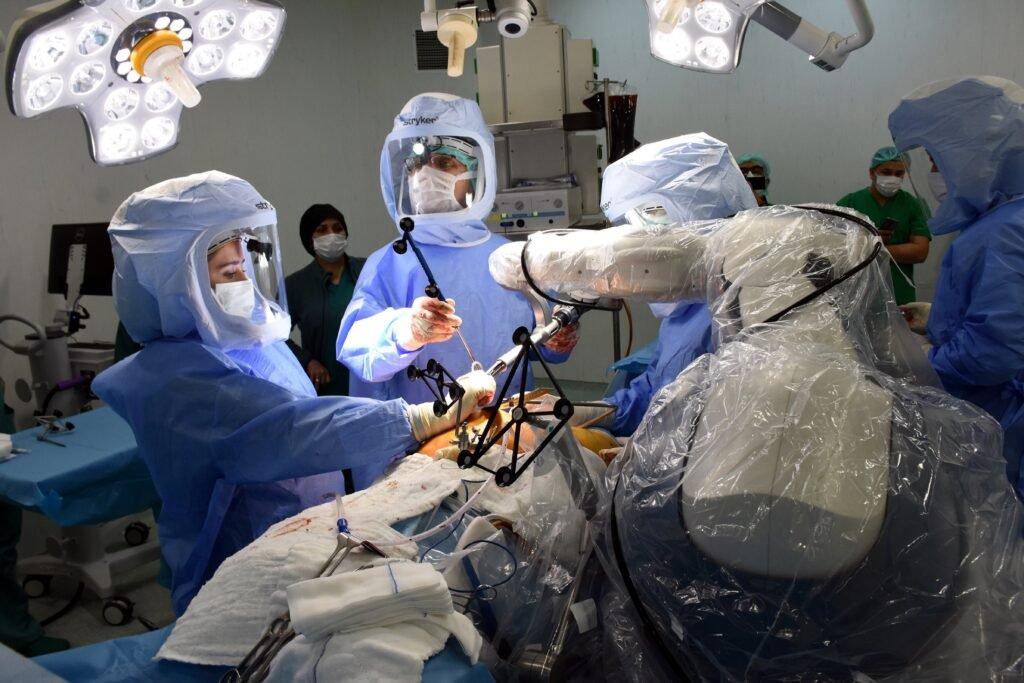
A state-of-the-art medical approach called robotic orthopedic surgery combines sophisticated imaging technology and robotics into orthopedic procedures. It outperforms conventional surgical techniques by giving surgeons exceptional precision and accuracy.
With the use of this technology, surgical outcomes are enhanced, including decreased pain, quicker healing periods, and fewer complications after surgery. With safer, more efficient, and customized treatment options available for a range of joint and bone procedures, this innovation has the potential to completely transform the field of musculoskeletal healthcare.
Types of Robotic Orthopaedic Surgery
Several robotic orthopedic surgery techniques are frequently employed, including:
1) Total Knee Arthroplasty (TKA): In this procedure, an artificial implant is used to replace the entire knee joint. The robotic system helps the surgeon place the implant precisely for maximum longevity and functionality.
2) Partial Knee Arthroplasty: This treatment replaces just the portion of the knee joint that is damaged. The implant is precisely aligned and placed with the assistance of the robot.
3) Total Hip Arthroplasty: This procedure uses an artificial implant to replace the hip joint. The exact positioning and alignment of the components are made easier by the robotic system.
4) Robotic Spinal Surgery: This refers to the use of robotic systems to help with decompression or spinal fusion operations. It aids in the accurate placement of rods, screws, and other implants.
5) Soft Tissue Surgery: This category includes procedures like tendon transfers and ligament repairs. The robot facilitates accurate tissue manipulation and suturing.
6) Robotic-Assisted Arthroscopy: To treat joint issues, arthroscopic procedures use a camera and tiny instruments inserted through tiny incisions. Robotic systems have the potential to improve these procedures’ accuracy.
7) Spinal Surgery: With robotic assistance, surgeons can perform spinal fusion, disc replacement, and deformity correction with greater accuracy and fewer incisions.
8) Robotic Total Shoulder Replacement: By helping to precisely position the shoulder implant, robotic systems can enhance joint function and lessen discomfort.
9) Robotic Joint Resurfacing: Using robotic technology, it is possible to preserve healthy bone and cartilage while resurfacing damaged joint surfaces in certain procedures.
10) Robotic-Assisted Fracture Surgery: Robotic systems can help with the accurate reduction and fixation of broken bones in cases of complex fractures.
Robotic orthopaedic surgery advantages
The advantages of robotic orthopedic surgery are numerous and strong.
1) Precision and Accuracy: By ensuring sub-millimeter accuracy in implant placement, robotic orthopedic surgery reduces errors.
2) Advanced Preoperative Planning: Surgeons can meticulously plan procedures and optimize results by using 3D models of a patient’s anatomy.
3) Minimally Invasive: Procedures using robotic assistance require fewer incisions, less pain, quicker healing times, and fewer complications.
4) Customization: The surgical plan is customized for every patient by the robot, which adjusts in real-time to unforeseen anatomical variations.
5) Decreased Radiation Exposure: The patient will receive less radiation since fewer intraoperative images are required.
6) Better Surgical Outcomes: Following surgery, patients have increased mobility and functionality, which improves their quality of life.
7) Shorter Hospital Stays: Shorter hospital stays are associated with lower healthcare costs because faster recovery times and fewer complications are common.
8) Continuous Learning: As robotic systems gather surgical data, ongoing analysis is made possible, allowing orthopedic care to be improved and refined.
9) Improved Patient Experience: In general, robotic orthopedic surgery provides a more individualized, safe, and efficient method of performing joint and bone operations.
In summary
An advancement in the field of joint and bone procedures is robotic orthopedic surgery. The precision, adaptability, and preoperative planning features of this technology are revolutionizing the way orthopedic surgeries are carried out. In the near future, robotic orthopedic surgery is expected to become the norm for a variety of orthopedic procedures due to continued research and development.
FAQs Regarding Orthopaedic Robotic Surgery
Q. How does orthopedic robotic surgery operate?
A. Using CT or MRI scans, precise 3D models of the patient’s anatomy are first created. Surgeons are aided by these models in their meticulous preoperative planning. In order to guarantee accurate implant placement and alignment, a robotic system guides the surgeon throughout the procedure and provides real-time feedback.
Q. What advantages does robotic orthopedic surgery offer?
A. There are several advantages to robotic orthopedic surgery, including
1) Enhanced accuracy
2) Diminished pain
3) Quicker healing periods
4) Less complicated
5) Personalized for the distinct anatomy of every patient
6) Additionally, it is less invasive, which means shorter hospital stays.
Q. Does robotic orthopedic surgery come with any risks?
A. Although robotic orthopedic surgery is generally regarded as safe, complications related to anesthesia and bleeding, as well as infection, are possible risks like any surgical procedure. But the accuracy and sophisticated planning of the technology can actually help to reduce many of these risks.
Q. For what patients is robotic orthopedic surgery appropriate?
A. A lot of patients find robotic surgery to be a flexible option, but whether it’s a good fit for them depends on a number of variables, including the particular procedure, the patient’s general health, and the surgeon’s recommendation. Your orthopedic surgeon will determine if this course of action is the most appropriate one for your situation.